Epiphora
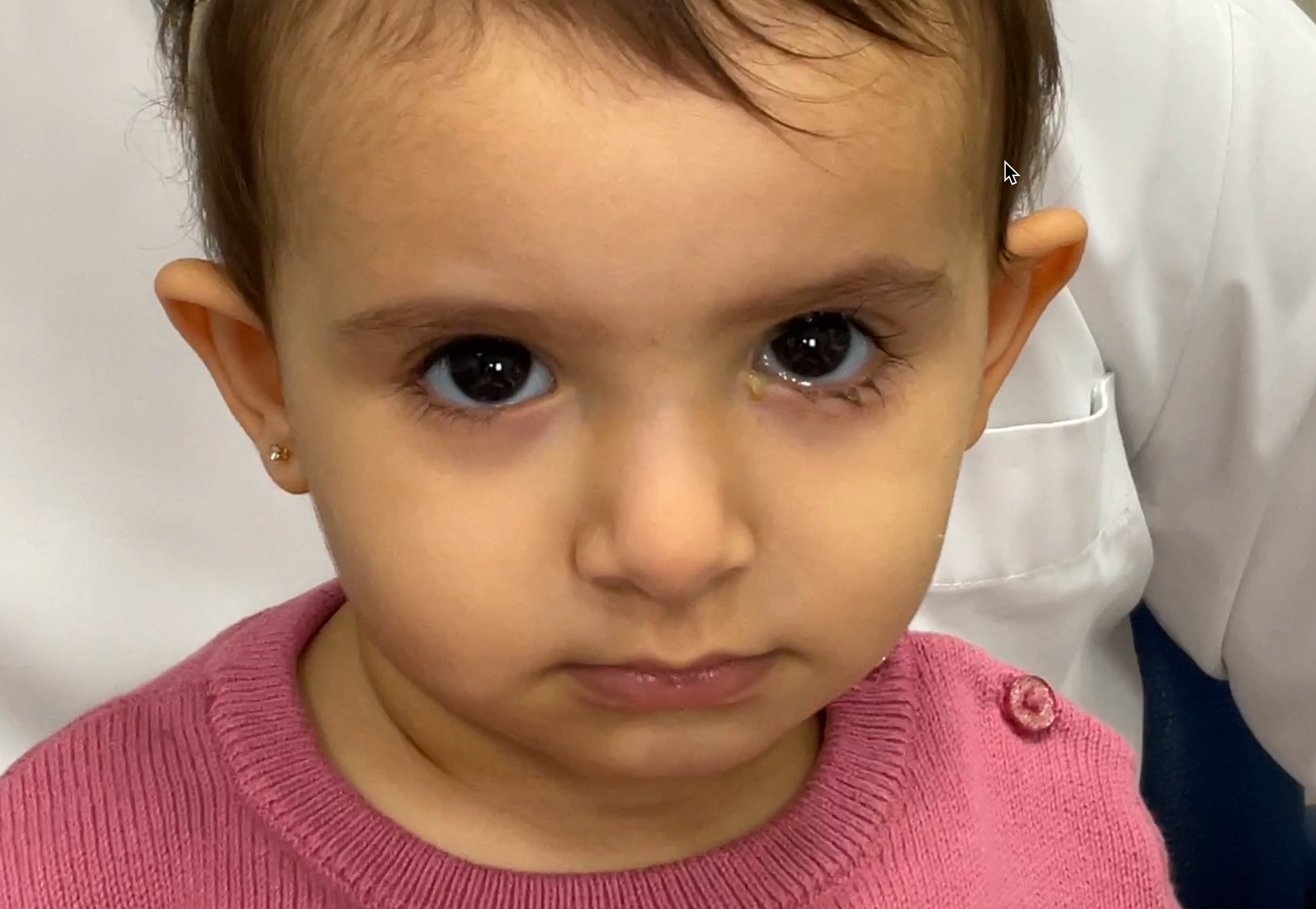
Epiphora
Tears are produced by special glands around the eyes, which help wash and moisturize the eyes, thus maintaining eye health.
Tears usually drain through small openings called lacrimal puncta, located on the inner side of both the upper and lower eyelids.
Through tiny tubes called lacrimal ducts, these puncta are connected to what is called the lacrimal sac.
The lacrimal sac is situated in the inner corner of the eye next to the nose, and through a bony channel called the nasolacrimal duct, tears are drained from this sac into the nasal cavity.
In the upcoming video, Dr. Ossama Abdelhakim explains the lacrimal system and why it may be blocked in some children ?
Among the main causes of excessive tearing in the eye are:
1- Blockage of oil Glands
There are small glands on the edge of the eyelid called Meibomian glands, which help maintain eye health by preventing rapid drying and keeping them moist.
2- Misdirection of eyelash growth
It is natural for upper eyelashes to grow upwards and lower eyelashes to grow downwards.
However, in some individuals, eyelashes may grow in the opposite direction, leading them to rubb against the eye, causing discomfort and excessive tearing.
Dr. Ossama Abdelhakim treats these abnormal eyelid conditions through surgery to correct the position of the eyelid under local anesthesia.
3- Narrowing of tear duct openings
This narrowing leads to difficulty in draining tears and accumulation of tears within the eye.
Dr. Ossama Abdelhakim treats these cases by injecting cortisone into the inner side of the eyelid near these openings.
This injection procedure is performed in the clinic after local anesthesia injection and is characterized by a high success rate in overcoming this narrowing, especially if the problem is diagnosed early.
Watch the upcoming video in which Dr. Ossama Abdelhakim explains how he treats this type of narrowed tear duct openings.
If this method fails or if the diagnosis is late, a minor surgery is performed to widen the tear drainage opening, usually in the operating room after local anesthesia injection.
4- Blockage of the nasolacrimal duct
This blockage prevents tears from draining. Treatment of nasolacrimal duct obstruction depends on the patient's age:
In young children:
The obstruction may resolve naturally, but a few children may require a simple surgical procedure.
In such cases, Dr. Ossama Abdelhakim performs dilation of the nasolacrimal duct using a specialized instrument under general anesthesia in the operating room, with the assistance of a specialized nasal endoscope to ensure the highest success of this probing procedure.
In the upcoming video, Dr Ossama Abdelhakim explains how he manages nasolacrimal duct obstruction in children.
In adults:
Usually obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct in adults is checked through a test performed in the clinic, where saline solution is injected through the nasolacrimal duct.
If the tear ducts are functioning normally, the saline solution can be tasted in the back of the throat. If they are blocked, the patient does not taste the saline solution in the throat.
Dr. Osama Abdelhakim manages cases of nasolacrima duct obstruction in adults through a surgical procedure called dacryocystorhinostomy, where a new channel is opened in the nasal bones to allow tears to drain into the nose.
This surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia. This surgery is performed through a small incision in the skin beside the eye, and this incision usually disappears without leaving a trace within a month or two.
In the upcoming video, Dr Ossama Abdelhakim explains how he manages nasolacrimal duct obstruction in adults.
It is normal for the eyes to tear at different times due to feelings of sadness or exposure to dust, but if tearing persists, seeking diagnosis and treatment requires choosing a specialized eye doctor.
At Dr. Ossama Abdelhakim's clinic, we strive to provide the best service for treating excessive tearing problems.


